Updated By: LatestGKGS Desk
Biology: The bacteriophage definition, structure and function, life cycle and effect
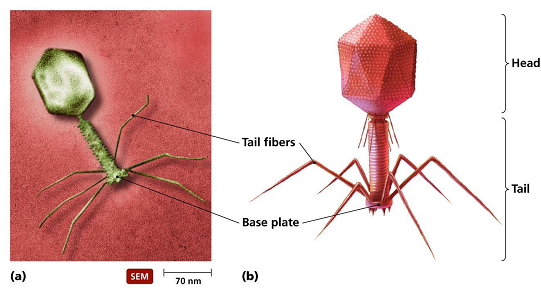
Biology: The bacteriophage definition, structure and function, life cycle and effect on plants and animals
A virus is a dangerous factor that can only replicate inside an animal host. Viruses can affect a variety of living organisms, including bacteria, plants, and animals.
Viruses are so delicate that a microscope is needed to visualize them, and all viruses are very modest If a virus bit is autonomous of its host, it consists of a viral genome, enclosed inside a protein shell called a capsid.
The bacteriophage is a kind of virus affects bacteria. In a particular, word "bacteriophage" actually indicates "bacteria eater," because bacteriophages kill their proprietor cells.
Each bacteriophage is made of a nucleic acid fragment that is enclosed by a protein composition. A bacteriophage associates itself to a sensitive bacterium and affects the proprietor cell.
Some affected, bacteriophage captures the bacterium's cellular plans to stop it from generating bacterial segments and alternately attacks the cell to give viral segments. Ultimately, original bacteriophages join and break outside of the bacterium, This method is called lysis.
Bacteriophages irregularly kill a part of their host cells' bacterial DNA while affecting the process and then shift this DNA inside the genome of unspoiled host cells. This method is called as transduction.


